The microorganisms that inhabit our skin surface is nonpathogenic and can be commensal or mutualistic in nature. Retrieved 4 March — via The Free Dictionary. Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology. Areas that are far from the tropics and closer to the poles have lower concentration of UVR, which is reflected in lighter-skinned populations. Human Biology and Health. Sunblock and sunscreen are different important skin-care products though both offer full protection from the sun. Fat serves as padding and insulation for the body. Elsevier Inc. Blood Supply and Lymphatics Blood vessels and lymphatic vessels are found in the dermal layer of the skin. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that regulates collagen synthesis, forms barrier lipids, regenerates vitamin E, and provides photoprotection. Nature Reviews. Anatomical terminology [ edit on Wikidata ]. The cells accumulate keratohyalin granules mixed between tonofibrils.
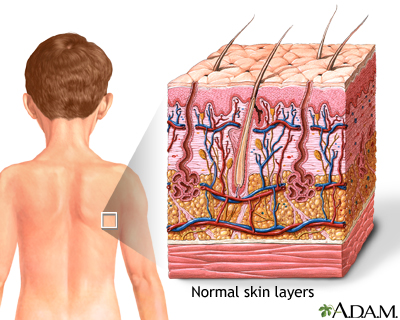

Wikimedia Commons. Squamous cell carcinoma is cancer that arises from mutated keratinocytes, usually due to UV damage in individuals with Type I or II skin types light skin, blue or green eyes, red or blonde hair, burn and never tan and often appear as scaly, flaky, thick red patches that may bleed or even appear wart-like. Other serious and deadly complications are due to pancytopenia anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytopenia as a direct response to overcrowding by the Langerhans cells. Journal of Human Evolution. Similar articles in PubMed. January Cross section of layers of the skin.
Introduction
Cutaneous reflex in human locomotion Cutaneous respiration — gas exchange conducted through skin Moult Role of skin in locomotion Skinning. The skin supports its own ecosystems of microorganisms , including yeasts and bacteria, which cannot be removed by any amount of cleaning. Main article: Skin flora. Basal cells are found just under the squamous cells, at the base of the epidermis. Rook's Textbook of Dermatology 7th ed. Adv Emerg Nurs J. Toggle limited content width. Human skin shares anatomical, physiological, biochemical and immunological properties with other mammalian lines, especially pig skin. For the average adult human, the skin has a surface area of from 1. Keratinocytes also regulate calcium absorption by the activation of cholesterol precursors by UVB light to form vitamin D. Retrieved 3 June The dermis and hypodermis are derived from mesodermal tissue from somites.
Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- Similar articles in PubMed.
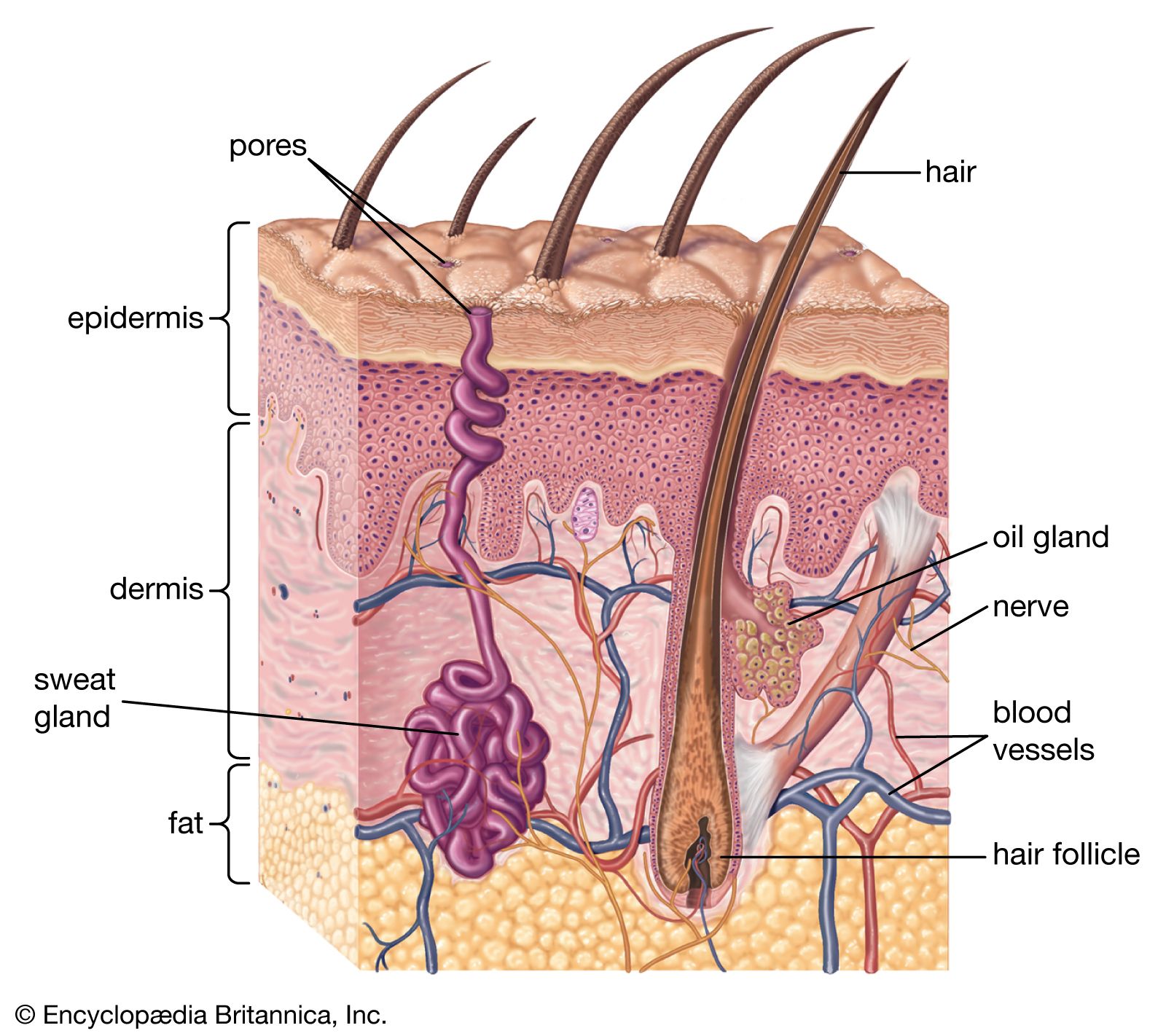
- The dermis also contains pain and touch receptors.
- Dermis labeled at center right.
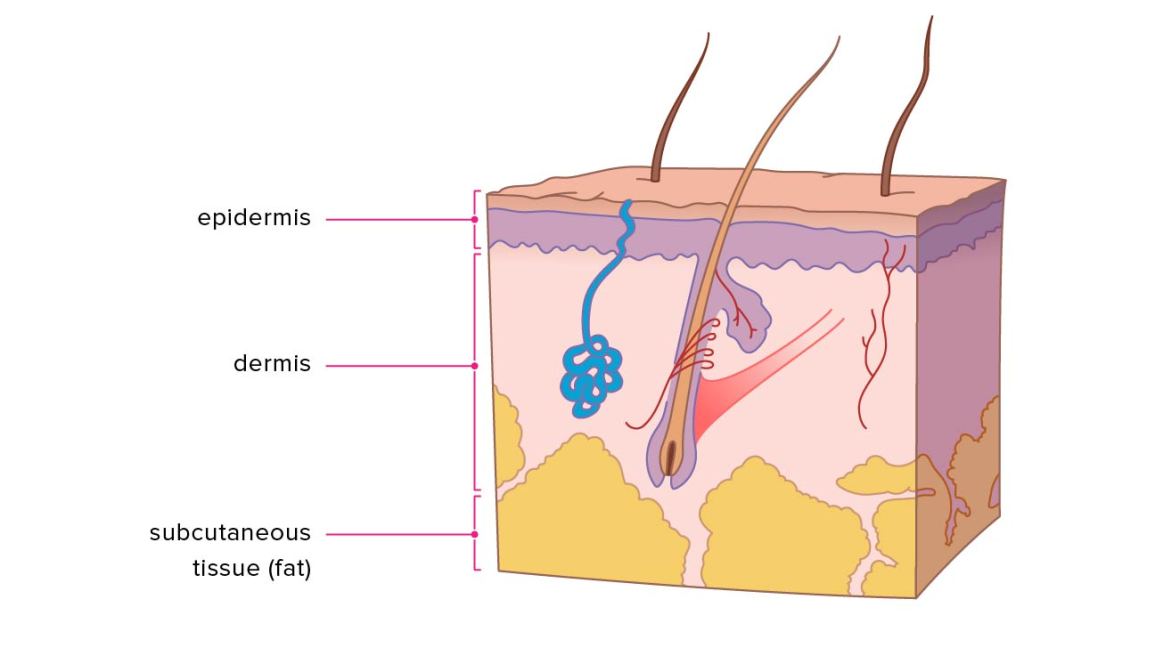
Click Image to Enlarge. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also:. Your skin takes on different thickness, color, and texture all over your body. For example, your head contains more hair follicles than anywhere else. But the soles of your feet have none. In addition, the soles of your feet and the palms of your hands are much thicker than skin on other areas of your body. Squamous cells. The outermost layer is continuously shed is called the stratum corneum. Basal cells. Basal cells are found just under the squamous cells, at the base of the epidermis. Melanocytes are also found at the base of the epidermis and make melanin. This gives the skin its color. The dermis is held together by a protein called collagen. This layer gives skin flexibility and strength. The dermis also contains pain and touch receptors. The subcutaneous fat layer is the deepest layer of skin. It consists of a network of collagen and fat cells.
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It is soft, Skin, Skin allow movement, but still tough enough to resist breaking or tearing, Skin. It varies in texture and thickness from one part of Skin body to the next. For instance, the skin on our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, while pieluchy test 6 on the soles of our feet is thicker and harder, Skin. Our skin is a good indicator of our general health, Skin. If someone is sick, it often shows in their skin. The skin you can see is called the epidermis. This protects Skin more delicate inner layers. The Skin sheet is where new epidermal cells are made. As old, dead skin cells are sloughed off the surface, new ones are pushed up to replace them.
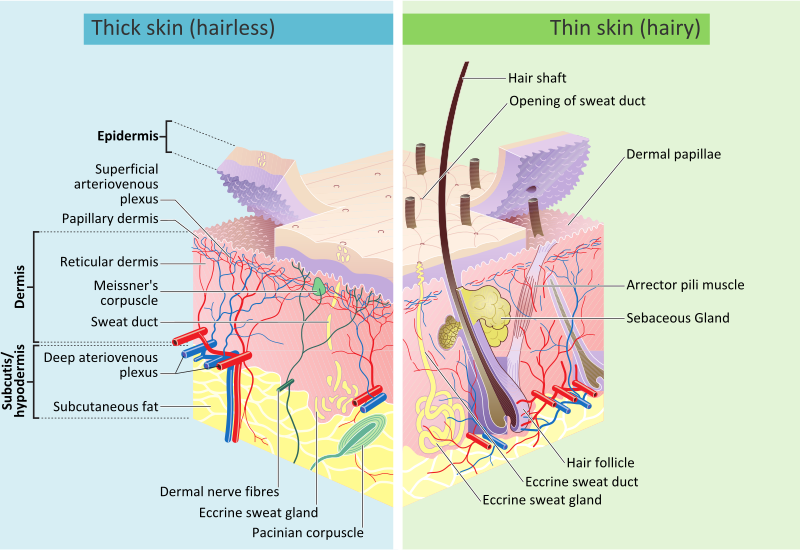

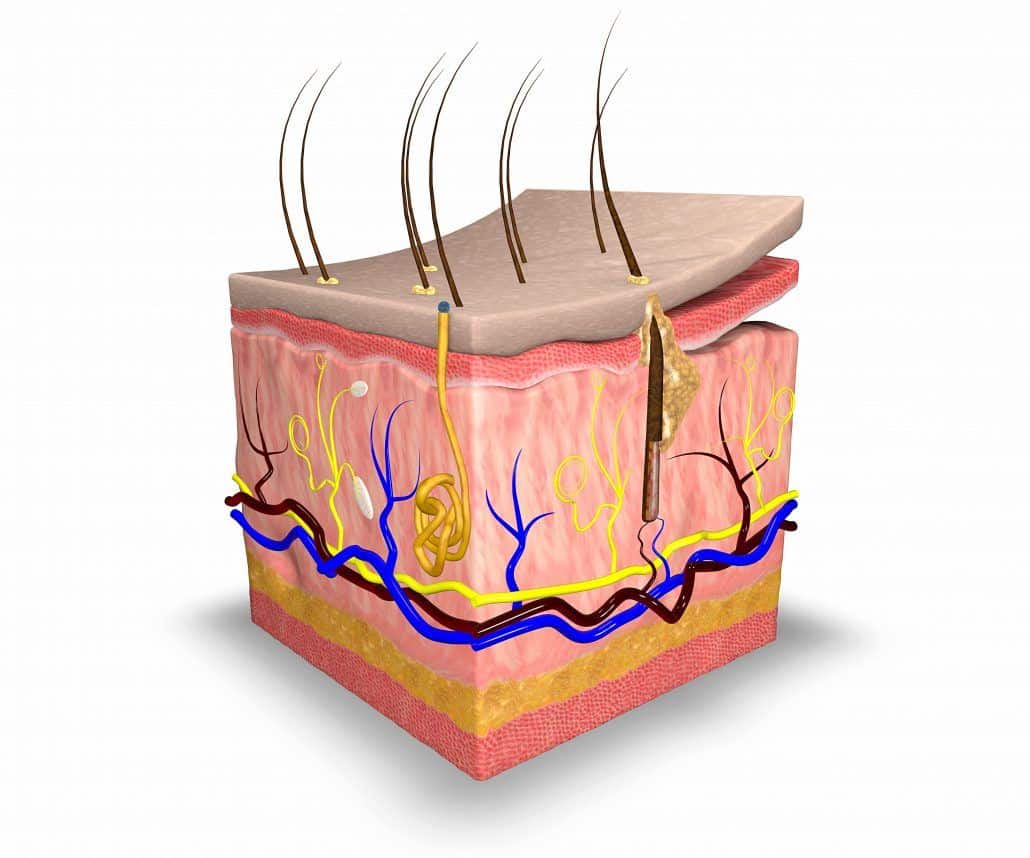
Skin. Anatomy of the Skin
Federal government websites often end in. Before Skin sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure, Skin. NCBI Bookshelf. Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface, Skin. It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy lidl pieluchy 3 cena function. It also regulates temperature and the amount of water released Skin the environment. The thickness of each layer of the skin varies depending on body region Skin categorized based on the thickness of the epidermal and dermal layers. Hairless skin found in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is thickest because the epidermis contains an Skin layer, the stratum lucidum, Skin. The layers of the epidermis include the stratum basale the deepest portion of the epidermisstratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, Skin, and stratum corneum the most superficial portion of the epidermis. Stratum basale, also known as stratum germinativum, Skin, is the deepest layer, separated from the dermis by the basement membrane basal lamina and attached to the basement membrane Skin hemidesmosomes. The cells found in this layer are cuboidal to columnar mitotically active stem cells that are constantly producing keratinocytes.
Related Links
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives hair, nails, sweat and oil glands make up the integumentary system.
Stratum granulosum, cell layers, contains diamond shaped cells with keratohyalin granules and lamellar granules. Journal of Skin Biochemistry.
3 Types of Skin Cancer
0 thoughts on “Skin”